Summary
Orange España, Spain’s second largest mobile operator, suffered a major outage on January 3, 2024. The outage was unprecedented due to the use of RPKI, a mechanism designed to protect internet routing security, as a tool for denial of service. In this post, we dig into the outage and the unique manipulation of RPKI.
On January 3, 2024, Spain’s second largest mobile operator, Orange España, experienced a national outage spanning multiple hours. The cause? A compromised password and an increasingly robust routing system. Turns out that the network operator’s favorite defense tool (RPKI) can be a double-edged sword.
Using a password found in a public leak of stolen credentials, a hacker was able to log into Orange España’s RIPE NCC portal using the password “ripeadmin.” Oops! Once in, this individual began altering Orange España’s RPKI configuration, rendering many of its BGP routes RPKI-invalid.
As demonstrated in our earlier analysis, the internet’s RPKI ROV deployment has reached the point where the propagation of a route is cut in half or more when evaluated as RPKI-invalid. Normally this is desired behavior, but when an RPKI config is intentionally loaded with misconfigured data, it can render address space unreachable, effectively becoming a tool for denial of service.
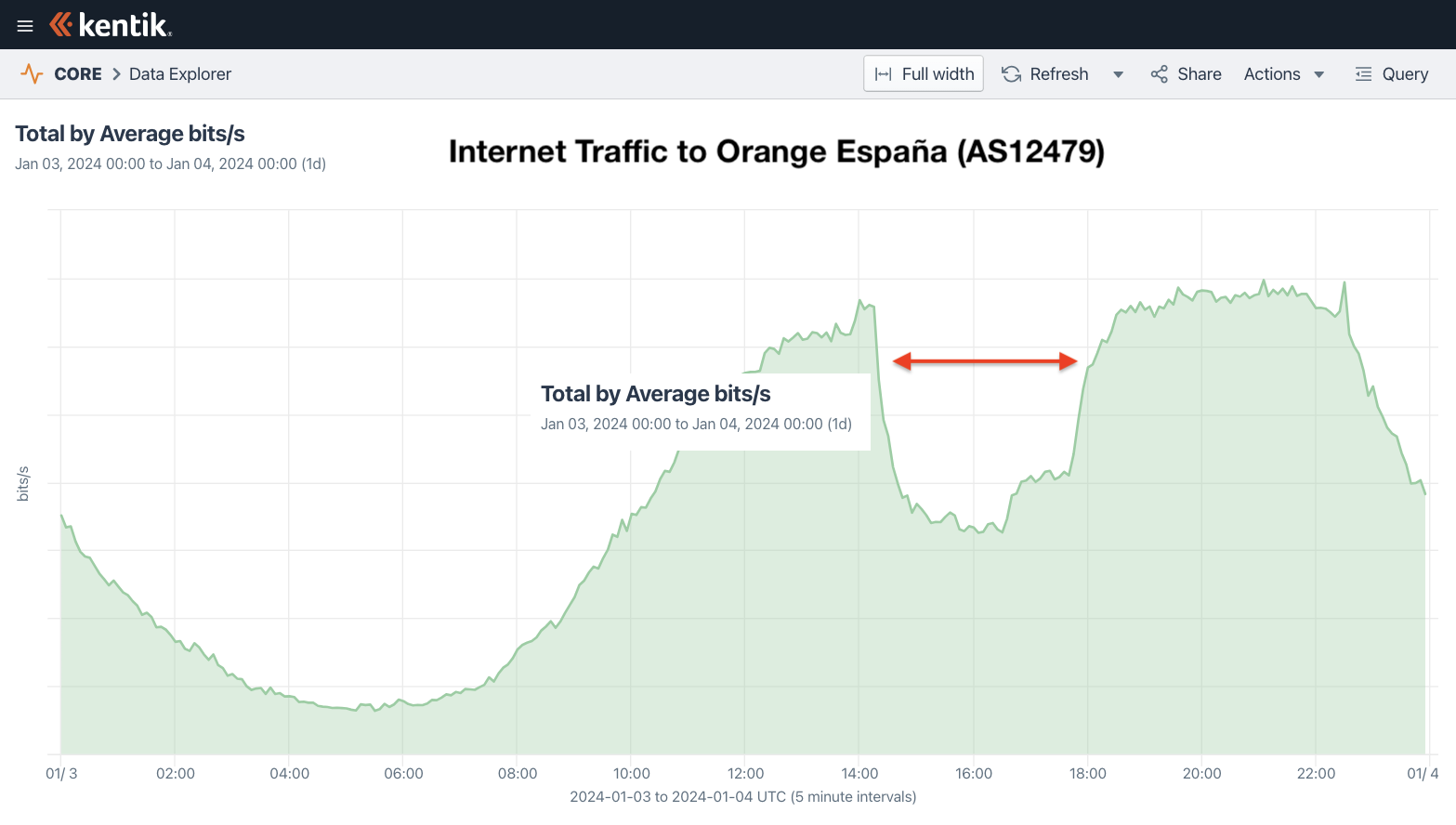
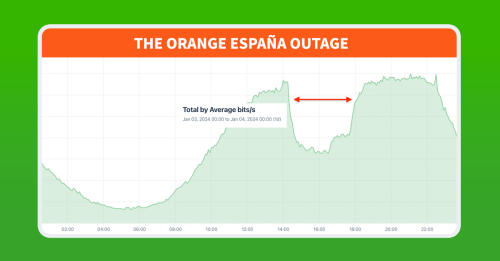
Using Kentik’s aggregate NetFlow, we observed the outage (illustrated above) as a large drop of the volume of inbound traffic to Orange España (AS12479) between 14:20 UTC (3:20pm local) and 18:00 UTC (7pm local). However, there were more developments prior to this window of time as well as some lingering effects, which we will dig into in the post below.
What happened?
We already know the outage took place and how the attacker pulled it off. Now let’s trace the sequence of events using archived RPKI data from RPKIviews.
The story begins at 09:28 UTC on January 3, when someone (presumably the attacker) began tinkering with publishing and revoking ROAs for IP ranges belonging to the Spanish mobile operator. Then, at 09:42 UTC they published three new ROAs for Orange España IP ranges with material impact.
Origin prefix maxLength ta expiration
AS12479 93.117.88.0/22 22 ripe 1704355258
AS12479 93.117.88.0/21 21 ripe 1704355258
AS12479 149.74.0.0/16 16 ripe 1704355258Given the fact that 93.117.88.0/22, 93.117.88.0/21, and 149.74.0.0/16 were all already originated by AS12479, those routes weren’t affected, but 149.74.0.0/16 had quite a few more-specifics that were now going to be evaluated as RPKI-invalid due to the max prefix length setting of 16.
Perhaps realizing this, minutes later, that someone published a slew of additional ROAs to account for the more-specifics of 149.74.0.0/16. These had the proper origin (AS12479) and as a result, all of those more-specifics became valid. All but one, that is.
Origin prefix maxLength ta expiration
AS12479 149.74.100.0/23 23 ripe 1704355258
AS12479 149.74.102.0/23 23 ripe 1704355258
AS12479 149.74.104.0/23 23 ripe 1704355258
AS12479 149.74.106.0/23 23 ripe 1704355258
AS12479 149.74.108.0/23 23 ripe 1704355258
(and many more)Using Kentik’s BGP visualization, we can compare the impact in reachability (aka propagation) for two adjacent more-specifics of 149.74.0.0/16. Shown below, 149.74.172.0/22 was the route missed in that follow-up publication of ROAs. Its reachability dropped for over four hours to as little as 20% of our BGP sources.

Conversely, the rest of the more-specifics looked like 149.74.168.0/22 below: a brief partial drop in reachability between the first and second publications of ROAs mentioned above.
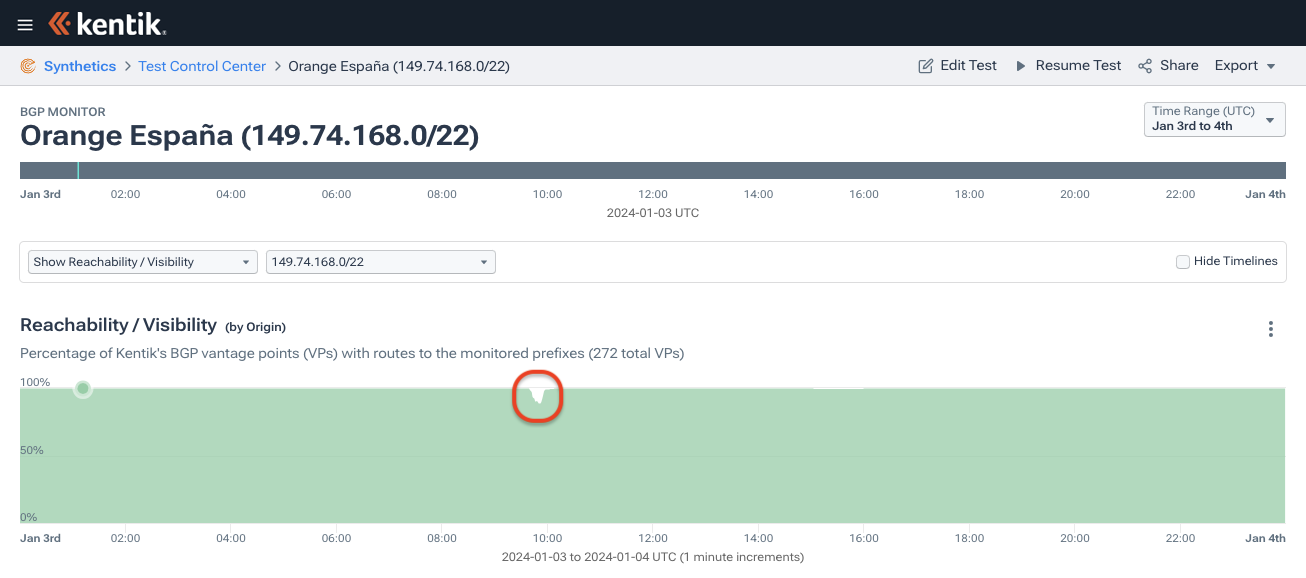
Although these prefixes were RPKI-invalid for several minutes, they only experienced a partial drop in reachability due to delays in the time to globally propagate ROAs, as documented in recent research on the topic. The act of blotting out a newly RPKI-invalid route is not instantaneous.
An effective BGP configuration is pivotal to controlling your organization’s destiny on the internet. Learn the basics and evolution of BGP.

Wielding RPKI as a weapon
Then the attacker took it a step further by creating ROAs with an origin other than that of Orange España’s. About the same time those additional ROAs were published covering the more-specifics of 149.74.0.0/16, four new ROAs were created for Orange España IP space with a deliberately incorrect origin of AS49581.
Origin prefix maxLength ta expiration
AS49581 149.74.0.0/16 16 ripe 1704355258
AS49581 1.178.232.0/21 21 ripe 1704355258
AS49581 145.1.240.0/20 20 ripe 1704355258
AS49581 62.36.0.0/16 16 ripe 1704355258The addition of the bogus ROA for 149.74.0.0/16 had no effect because the attacker had previously created a ROA with the correct origin (AS12479) — as long as one ROA matches, a route is evaluated as RPKI-valid.
145.1.240.0/20 and 1.178.232.0/21 were only briefly invalid before the attacker published ROAs with correct origins.
Origin prefix maxLength ta expiration
AS12479 145.1.240.0/20 20 ripe 1704355258
AS12479 1.178.232.0/21 21 ripe 1704355258Only 62.36.0.0/16 (shown below) and its numerous more-specifics were rendered RPKI-invalid and had their reachability reduced for the duration of the outage due to the ROAs with bogus origins.
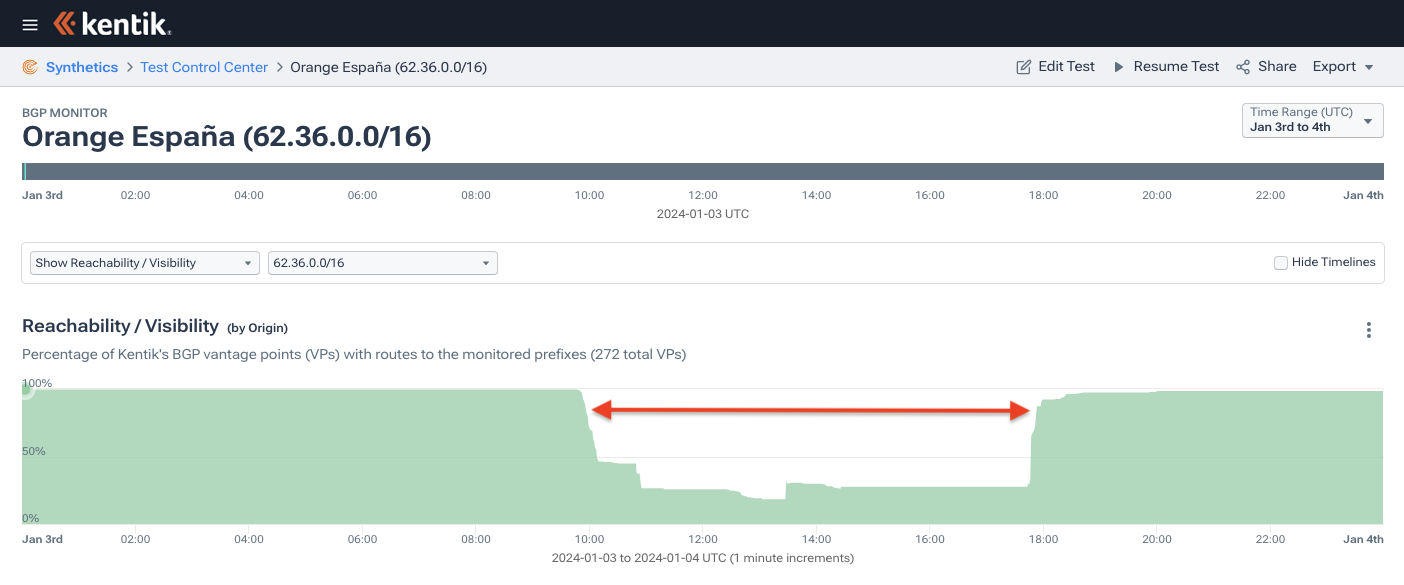
Thus far in the story, the attacker’s tinkering has led to the creation of a couple of RPKI-invalid routes and some minor reachability problems, but the major disruption was yet to come.
It wasn’t until about 14:20 UTC (3:20pm local) that things got ugly. The attacker went for it and published four more ROAs with bogus origins. Two of the ROAs were /12’s which covered over a thousand routes originated by AS12479 — all rendered RPKI-invalid by the publication of the following ROAs:
Origin prefix maxLength ta expiration
AS49581 85.48.0.0/12 12 ripe 1704355258
AS49581 90.160.0.0/12 12 ripe 1704355258
AS49581 93.117.88.0/21 21 ripe 1704355258
AS49581 145.1.232.0/21 21 ripe 1704355258It was here when the traffic graph at the beginning of this blog post began to take a nose dive. The number of globally routed routes originated by AS12479 dropped from around 9,200 to 7,400, as backbone carriers which reject RPKI-invalid routes stopped carrying a large chunk of Orange España’s IP space.
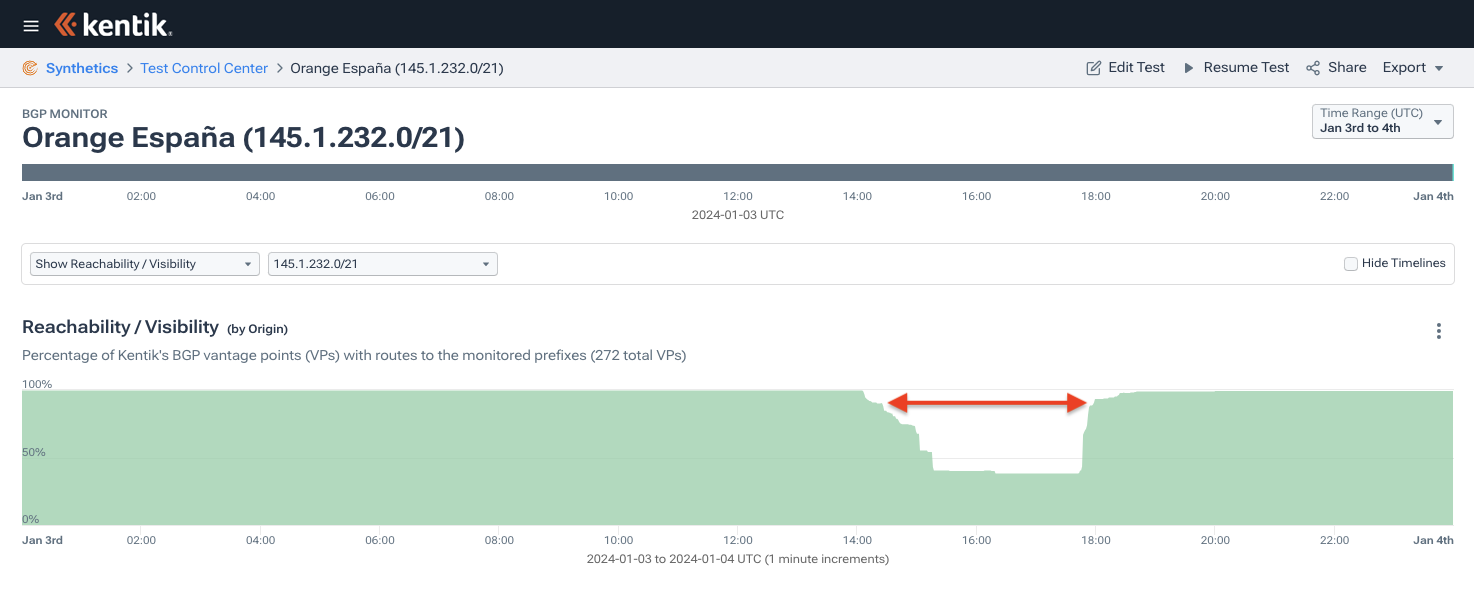
It wasn’t until just before 18:00 UTC (7pm local) that things began to return to normal. Engineers from Spain’s second largest mobile operator regained control of their RIPC NCC account and began publishing new ROAs that would enable the carrier to restore service.
Origin prefix maxLength ta expiration
AS12479 85.48.0.0/12 12 ripe 1704384768
AS12479 90.160.0.0/12 12 ripe 1704384768
AS12479 62.36.0.0/16 16 ripe 1704384768
AS12479 93.117.88.0/21 21 ripe 1704384768
AS12479 145.1.232.0/21 21 ripe 1704384768
AS12479 93.117.92.0/22 22 ripe 1704384768
AS12479 62.36.21.0/24 24 ripe 1704384768Conclusion
While RPKI was employed as a central instrument of this attack, it should not be construed as the cause of the outage any more than we would blame a router if an adversary were to get ahold of the login credentials and start disabling interfaces.
It seems that prior to January 3, the Spanish mobile operator’s RIPE NCC account had never created a ROA (although other parts of Orange had created some on its behalf). If RPKI wasn’t on Orange España’s radar before, it sure is now.
Although the outage is over, there is still a lot of clean-up work to be done. As of this writing, over a thousand of the routes originated by AS12479 are still invalid, mostly due to the max prefix length setting on the ROAs for the two /12’s. Between yesterday and today, the number of unique IPv4 addresses originated by AS12479 dropped from 7 million to 5 million, and a few bogus ROAs with an origin of AS49581 are still in circulation.
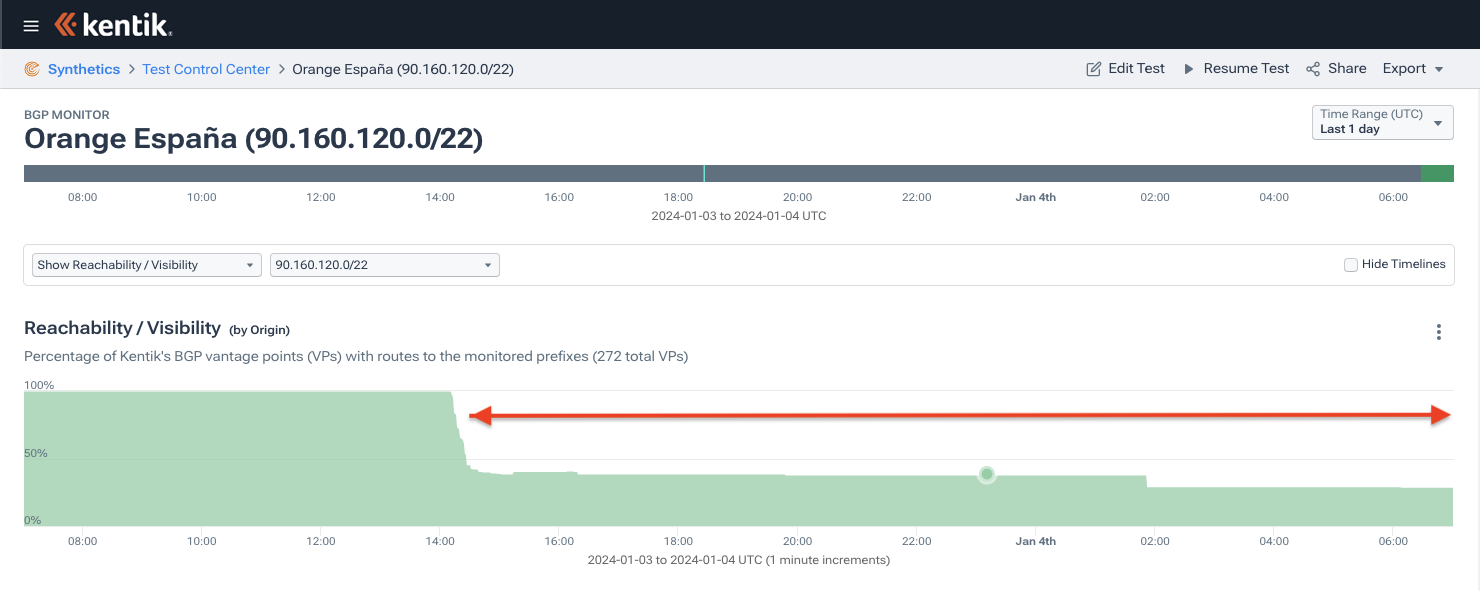
I would remind those engineers cleaning up the ROAs that max prefix length is an optional field and can simply be left empty causing RPKI to only match on the origin of the ROA. This course of action was recently published as a best current practice.
RIPE NCC, the RIR responsible for managing the allocation and registration of internet number resources (IP addresses and ASNs) in Europe, has launched an investigation into the incident.
Hopefully this incident can serve as a wake-up call to other service providers that their RIR portal account is mission-critical and needs to be protected by more than a simple password.
UPDATE: 16 Jan 2024
In our original blog post, I mentioned some “clean-up work” that was still required to address a myriad of RPKI-invalid routes that were being originated by AS12479 due to the quick fix ROA modifications that resolved the outage.
These RPKI-invalid routes weren’t causing connectivity issues because three covering routes (85.48.0.0/12, 90.160.0.0/12 and 62.36.0.0/16) were RPKI-valid ensuring the address space was globally reachable.
Well, that clean-up work was accomplished at 16:00 UTC on January 8, five days after the multi-hour outage. Orange España modified the ROAs for these three IP address ranges by increasing the maximum prefix length to 24 (from 12 and 16).
We can see the impact in BGP as the reachability of some of the formerly RPKI-invalid routes jumped once they were RPKI-valid and no longer being filtered. The graphic below shows how reachability through the upstreams of AS12479 (primarily Orange, AS5511 and Lumen, AS3356) changed over this time:
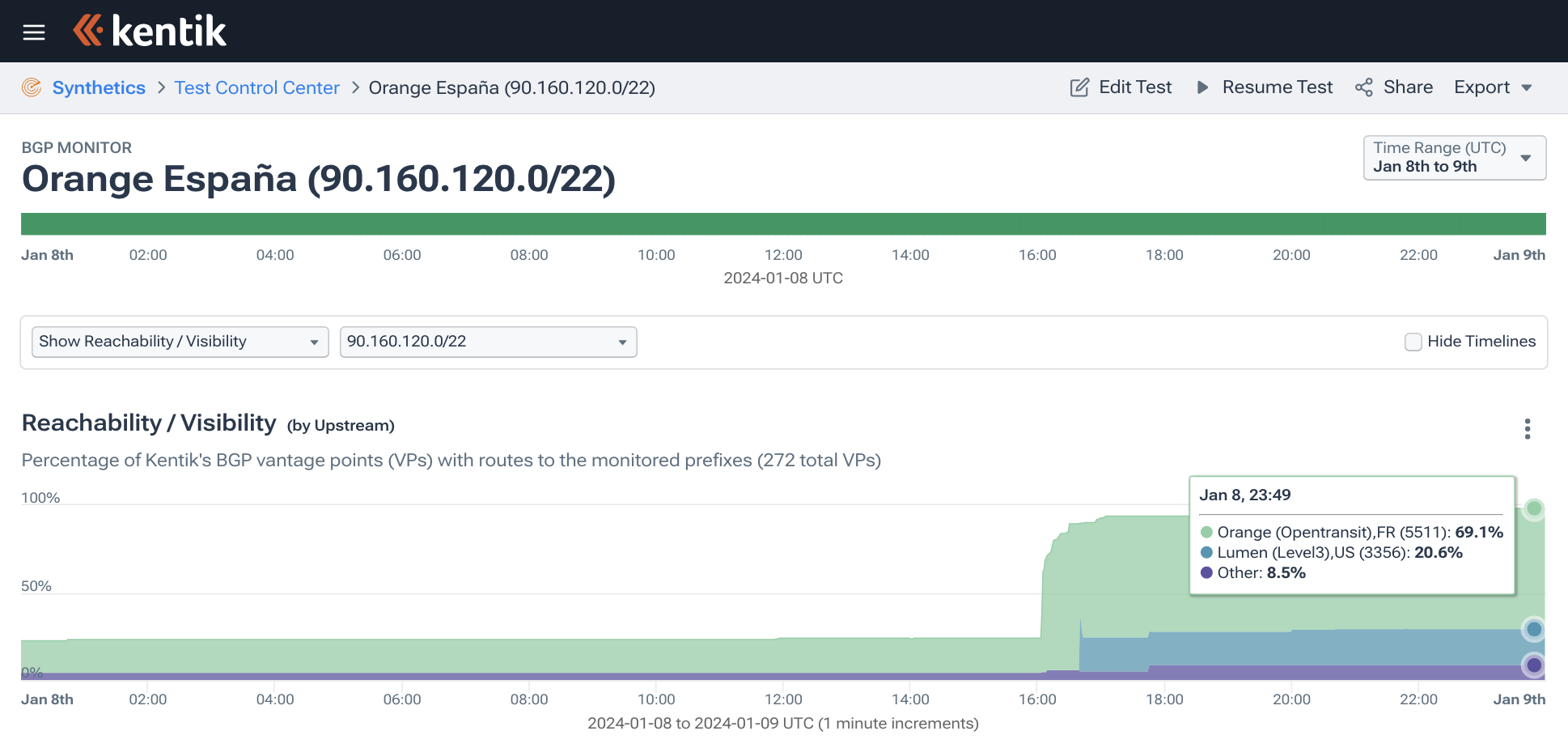
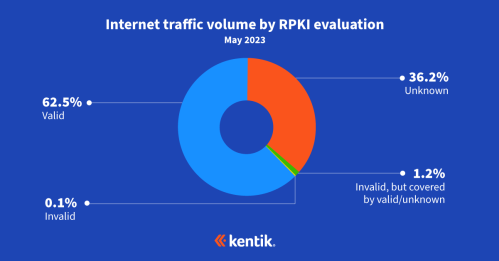
The change is also visible in Kentik’s aggregate NetFlow. Below is a graphic of traffic to AS12479 (in bits/sec) on January 8 colored by the RPKI evaluation of the destination address space.
There are three categories to traffic:
- RPKI-unknown (routes without ROAs)
- RPKI-valid (routes which match ROAs)
- RPKI-invalid, but covered (routes which are RPKI-invalid, but are reachable via a covering prefix)

We can see the “RPKI-invalid, but covered” traffic, along the bottom in a faint yellow, drops away to zero once the changes to the ROAs are published and that traffic becomes RPKI-valid. Again, since there were RPKI-valid covering routes, there was no change in the overall volume of traffic reaching AS12479.
How to protect your RIPE NCC account
How to Enable Two Step Verification on a RIPE NCC Access account
Thanks to Job Snijders of Fastly for his expert guidance on this blog post.