NAT Gateways: A Guide to Cost Management and Cloud Performance
NAT Gateways (Network Address Translation gateways) are essential components in cloud computing environments. They enable resources in a private subnet to connect to the Internet or other cloud services while preventing the Internet from initiating connections with those resources.
A NAT Gateway is analogous to the internet router in a home network. In a home network, multiple devices are connected, such as laptops, phones, and smart home devices. To access the internet, these devices use a single router that assigns them private IP addresses, while the router itself uses a public IP address to communicate with the outside world. In cloud computing, a NAT Gateway plays a similar role. It allows resources in a private subnet to access external services, like the internet, by translating private IP addresses to a public one, while blocking unsolicited inbound connections for enhanced security.
This article provides an overview of NAT Gateways, explaining their function, importance, and use cases in cloud computing environments. It compares implementations across major cloud providers, explores common challenges associated with metered services, and explains how Kentik’s network observability solution can help manage and optimize NAT gateways to enhance security, reduce costs, and improve network performance.
What is a NAT Gateway?
A NAT Gateway is a Network Address Translation service that enables instances in a private subnet to access the internet or other external services, while preventing external services from initiating connections with those instances. It translates the instances’ private IP addresses to a public IP address, ensuring secure and efficient outbound traffic without exposing the instances to unsolicited inbound connections.
Here, “instances” refers to virtual machines (VMs) or other computing resources that run applications within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). These instances are the actual servers or machines that handle processing tasks, data storage, and application workloads. The NAT Gateway enables these instances to connect to external services, such as the internet, while keeping them secure by blocking incoming traffic that wasn’t requested by the instances themselves.
How Do NAT Gateways Work?
Understanding the basic mechanisms of NAT gateways helps clarify their role in cloud architecture and the benefits they provide in terms of security, scalability, and cost management. Core concepts include:
- Network Address Translation (NAT): NAT is a process where one or more local IP addresses are translated into one or more global IP addresses and vice versa. In the context of a NAT gateway, private IP addresses within a subnet are translated into a public IP address, allowing outbound internet access.
- Outbound Traffic: Instances within a private subnet can send traffic to the internet through the NAT gateway. The NAT gateway translates the private IP addresses of the instances to the public IP address of the NAT gateway.
- Inbound Traffic: The NAT gateway does not allow unsolicited inbound connections from the internet to the instances within the private subnet. This provides an additional layer of security by protecting instances from external threats.
Use Cases for NAT Gateways
Typical applications of NAT gateways in cloud environments include:
- Web Servers and Databases: When you want to keep databases and backend servers in a private subnet but still need to download updates or patches from the internet.
- Bastion Hosts: When providing a secure gateway to administer instances in private subnets without exposing those instances directly to the internet.
- Application Servers: When your application servers need to communicate with external services (e.g., payment gateways, APIs) without exposing them directly to the internet.
Benefits of NAT Gateways in Cloud Environments
NAT gateways provide several important benefits in cloud networking, including:
- Security: Using a NAT gateway protects instances in private subnets from direct exposure to the internet. This reduces the attack surface and enhances the security of the cloud environment.
- Scalability: NAT gateways are managed services provided by cloud providers (e.g., AWS). They automatically scale up to accommodate varying levels of traffic, ensuring reliable and consistent performance without the need for manual intervention.
- High Availability: NAT gateways are designed to be highly available. They are deployed in multiple Availability Zones (AZs) for redundancy, ensuring no single point of failure exists.
- Simplified Management: Cloud providers manage NAT gateways, relieving users from the burden of maintaining and patching the underlying infrastructure. This allows users to focus on their applications and workloads.
- Cost Efficiency: By using NAT gateways, users can optimize their costs. Instead of assigning public IP addresses to each instance, which can be costly, users can use a single NAT gateway to provide internet access to multiple instances. However, improperly configured NAT gateways can have hidden costs as described below.
Challenges with Metered Services and Data Costs in Cloud Environments
While essential for enabling secure outbound traffic from private subnets, NAT gateways can lead to significant costs, especially in environments with high data transfer volumes. Metered services like NAT gateways charge not only for the service itself but also based on the volume of data transferred through it. For example, AWS charges $0.045 per hour for the gateway and an additional $0.045 per GB of traffic, which can quickly add up to substantial expenses in large-scale deployments.
While NAT gateways offer crucial benefits like security and connectivity, misconfigurations can lead to significant costs. For example, routing traffic through a NAT gateway instead of a more cost-effective route can quickly escalate expenses.
-
Data Egress Costs: Data leaving the cloud (egress) often incurs substantial charges, especially when transferring large volumes across regions or cloud providers. These costs can add up unexpectedly, particularly in multi-cloud environments where data frequently moves between different cloud services.
-
Cost Optimization: To mitigate these costs, it’s essential to carefully monitor and analyze traffic patterns, configure services correctly, and choose the proper routes for data transfer. Tools like Kentik provide visibility into these metrics, allowing you to optimize data flow and prevent unnecessary expenses.

An Overview of NAT Gateways Across Major Cloud Providers
AWS
AWS offers both Public and Private NAT Gateways. Public NAT gateways enable instances in private subnets to access the internet, while private NAT gateways are used to connect instances to other VPCs or on-premises networks. Public NAT gateways require an Elastic IP and reside in public subnets, whereas private NAT gateways do not require an Elastic IP and operate in private subnets.
For more detailed information, visit the AWS VPC NAT Gateway documentation.
Microsoft Azure
Azure NAT Gateway is a fully managed service that provides outbound internet connectivity for virtual machines and other Azure resources in a private subnet. It automatically scales to meet outbound traffic demands and reduces the risk of SNAT port exhaustion. Azure NAT Gateway offers simple setup, security through static public IP addresses, and high resiliency with software-defined networking. It supports up to 16 public IP addresses and integrates seamlessly with Azure Firewall for additional security.
For more detailed information, visit the Azure NAT Gateway documentation.
Google Cloud
Google Cloud NAT is a managed network service that enables resources in private subnets to create outbound connections to the internet or other networks. It supports both Public NAT for internet connectivity and Private NAT for private-to-private network communications. Cloud NAT is implemented using Google’s Andromeda software-defined networking, offering benefits such as automatic scaling, security, high availability, and integration with Google Cloud services like Cloud Monitoring for metrics and logging.
For more details, visit the Google Cloud NAT documentation.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
OCI’s NAT Gateway provides instances in private subnets with secure outbound internet access while preventing inbound connections initiated from the internet. It supports TCP, UDP, and ICMP traffic and routes outbound traffic by assigning a public IP address to the NAT gateway. The NAT gateway is highly available and integrates with OCI’s networking services, allowing for secure and scalable internet access without exposing private instances to external threats.
For more details, visit the Oracle Cloud NAT Gateway documentation.
By understanding the nuances of each provider’s NAT Gateway implementation, you can make informed decisions based on your specific network architecture and security needs.
How Kentik Helps Address Common Challenges with NAT Gateways
Managing NAT gateways in cloud environments can be challenging due to the complexity of metered services, misconfigurations, and the difficulty in tracking and optimizing costs. One of the primary challenges is the unexpected costs that can arise from misconfigurations, such as routing traffic through a NAT gateway instead of an Internet gateway, leading to higher charges.
In this video, Kentik enterprise solutions architect Mike Mike Krygeris demonstrates how Kentik’s platform can monitor and analyze traffic through NAT gateways. He shows a visual representation of an AWS environment where NAT gateways are actively used, and how Kentik tracks traffic flows between different entities. The demonstration highlights Kentik’s ability to filter and drill into traffic data associated with NAT gateways, identify spikes, and set baselines for normal traffic levels. This helps in detecting anomalies and optimizing traffic to reduce costs, ensuring efficient cloud resource management.
In his demonstration, Mike shows a variety of Kentik features that can help NetOps professionals effectively manage NAT gateways, optimize cloud costs, and prevent costly misconfigurations:
-
Visibility into Traffic Flows: Kentik provides detailed insights into traffic patterns, allowing you to see where traffic is going and identify inefficiencies that could lead to unexpected costs. By tracking traffic through NAT gateways and monitoring egress traffic, Kentik helps you catch misconfigurations early, preventing costly mistakes.
-
Cost Optimization: Kentik offers tools to analyze and optimize cloud costs by providing detailed visibility into NAT gateway usage. This includes setting baselines and alerts for traffic volumes, enabling you to monitor for unusual spikes that could result in higher costs.
-
Anomaly Detection and Alerting: With Kentik’s real-time monitoring and alerting, you can detect anomalies in traffic that may indicate misconfigurations or inefficiencies. By setting thresholds based on historical data, you can minimize false positives and focus on real issues that need attention.
-
Unified Monitoring Across Multi-Cloud Environments: For organizations using multiple cloud providers, Kentik’s cloud-agnostic platform unifies monitoring and provides a single view of traffic across all environments. This simplifies the management of NAT gateways and other network resources, ensuring that you have comprehensive visibility and control.
Transitioning to cloud quickly complicates networking. Learn the top 3 AWS gotchas and how to avoid them.

Kentik Solutions for Managing NAT Gateways
Kentik offers several features to enhance the management and optimization of NAT gateways in cloud environments.
Enhanced Visibility into NAT Address Tracking
Kentik provides detailed visibility into NAT operations by tracking both pre-NAT and post-NAT addresses. This helps network operators identify and resolve issues related to network address translation and ensures accurate traffic analysis. Understanding the original source and destination of traffic is essential for cloud network troubleshooting and security analysis.
Manage and Reduce NAT Gateway Costs
By analyzing traffic patterns and usage, Kentik can help identify inefficiencies and unnecessary costs associated with NAT gateways. These capabilities include identifying underutilized resources and providing insights to reduce costs:
- Traffic Volume Analysis: By providing detailed insights into traffic volumes through NAT gateways, Kentik helps identify cost drivers and optimize the use of NAT gateways to reduce unnecessary costs.
- Cost Visibility: Kentik’s observability tools offer granular visibility into network costs, allowing for better financial management and identifying potential areas for cost savings.
- Lower MTTR: Lower mean-time-to-resolution for identifying and mitigating sudden traffic spikes due to misconfigurations.
In this short video, Kentik’s Phil Gervasi explains how AWS NAT gateways are essential, but also costly—especially when they’re underutilized or overused. He shows how Kentik can be used to quickly identify unnecessary NAT gateway expenses and optimize cloud infrastructure spending:
Real-time Network Performance Monitoring
Kentik offers real-time monitoring of network performance, including traffic through NAT gateways. This helps detect performance bottlenecks, potential security threats, and optimize the overall multicloud network performance. By monitoring traffic patterns, Kentik can also identify anomalies (deviations from normal/baseline network behavior) that may indicate performance issues or security threats.
Security Enhancements
With comprehensive traffic visibility, Kentik enhances network security by identifying unusual or unauthorized traffic passing through NAT gateways. This helps in the early detection and mitigation of security incidents. Kentik’s alerting and reporting tools can alert network operators to unusual traffic patterns that may indicate security breaches or misconfigurations.
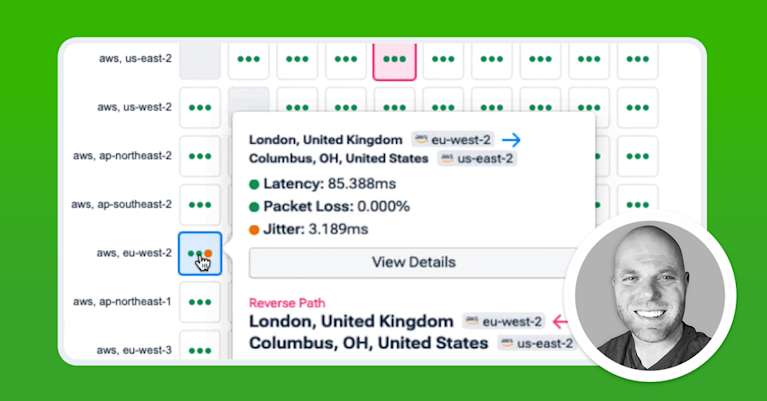
NAT Gateway Route and Path Analysis
Kentik provides detailed path analysis and routing information, helping network operators understand the flow of traffic through NAT gateways and optimize routing policies. Kentik provides a unified view of network traffic, including flows through NAT gateways, simplifying network management and improving operational efficiency.
By leveraging these capabilities, Kentik helps organizations ensure their NAT gateways are efficiently managed, secure, and cost-effective, contributing to their cloud network environments’ overall health and performance.
Learn More About Using Kentik for NAT Gateway Observability
Kentik offers a suite of advanced network monitoring solutions designed for today’s complex, multicloud network environments. The Kentik Network Observability Platform empowers network pros to monitor, run and troubleshoot all of their networks, from on-premises to the cloud. Kentik’s network monitoring solution addresses all three pillars of modern network monitoring, delivering visibility into network flow, powerful synthetic testing capabilities, and Kentik NMS, the next-generation network monitoring system.
To see how Kentik can bring the benefits of network observability to your organization, request a demo or sign up for a free trial today.